|
SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM |
|
|

|
Origin
Components
- Myelinated fibres emerge through ventral roots of corresponding spinal nerves
- Join spinal nerve trunks
- White rami communicante
- Sympathetic trunks- inter connected ganglia
Distribution of postganglionic fibres
- Plexuses on arteries
- Spinal nerves
- Cranial nerves
- Directly
Targets
- Glands
- Smooth / cardiac muscle
|
|
| Parts of sympathetic trunk |
|
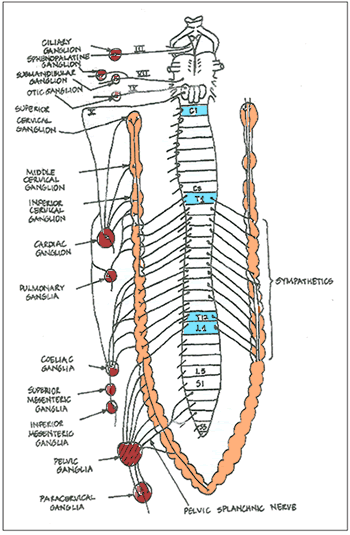 |
Cervical part
- Receive preganglionic fibres T1- T5
- Lies on the pre-vertebral muscles behind the carotid sheath.
- Three interconnected ganglia respectively known as superior, middle and inferior cervical sympathetic ganglia
- Post ganglionic fibres distributed with neighboring arteries to head, neck and upper limb
Thoracic
- Receives preganglionic fibres T1- T5
- Lies on the necks of the ribs in the upper part of the thorax and the sides of the vertebra in the lower part.
- Behind pleura
- Distributed to thoracic visceral
Abdominal
- T6- T12
- Lies on the anterolateral surface of the lumbar vertebrae
- Right trunk lies behind the inferior vena cava
- Crosses sacral promontory to become continuous with the pelvic trunk.
- Distributed to abdominal viscera.
The Pelvic
- Pelvic splanchnic L1-L2
- Downwards on the pelvic surface of the sacrum,
- The two trunks usually unite in front of the coccyx and end in a small-unpaired ganglion (ganglion impar).
|
|
|
Autonomic ganglia and plexus |
|
|
Thorax
Cardiac and pulmonary
Abdomen
Celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric
Pelvic
Hypogastric
|
| |
|
|
