The large Intestine |
|
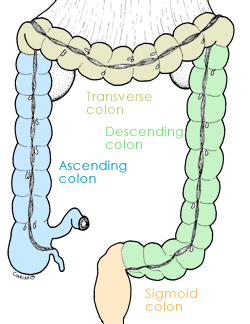 |
It consists of the following parts:
- Caecum and appendix
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
- Descending colon
- Sigmoid colon
- Rectum
Note:
- The ascending and descending colon are usually devoid of a mesocolon, or both, may be present.
- A transverse mesocolon and sigmoid mesocolon are always present.
|
| |
|
|
| The caecum |
|
 |
Position
- Lies in the right iliac fossa, below the ascending colon
- Upper end continues into the ascending colon at the intertubercular plane.
- It opens into the upper most part of its medial aspect, the opening being guarded by the ileocaecal valve.
- About 2.5 cm below the ilecaecal junction, the vermiform appendix opens into its medial aspect.
Posterior relations
- The iliacus muscle and its fascia, psoas major.
- The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh, genitofemoral nerve
.
- The femoral nerve and the gonadal vessels.
|
| |
|
| |
|
| The ascending colon |
|
- Continuous below with the upper end of the caecum at the intertubercular plane.
- Ascends on the posterior abdominal wall to reach the right lobe of the liver, where it turns to the left and downwards as the right colic flexure.
- About 12.5 – 15 cm long.
- Posterior surface is usually devoid of a serous coat, but the ascending colon may retain an ascending mesocolon.
- Posteriorly, the ascending colon lies on:
(+)
Iliacus
(+)
Quadratus lumborum
(+) Ilio-inguinal
(+)
Iliohypogastric nerves
(+)
Lower part of the right kidney.
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| The right colic flexure |
|
- Lies on the lower part of the right kidney and the descending part of the abdomen.
- In front and above it is in contact with the colic impression on the right lobe of the liver.
- Slightly below the transpyloric plane.
|
| |
|
|
The transverse colon |
|
- Extends across the abdominal cavity from the right colic to the left colic flexure.
- The greater omentum is attached to its anterior taenia and the transverse mesocolon to its superior taenia, thus completing the curtain between the supracolic and infracolic compartments of the greater sac.
- The anterior aspect of the transverse colon forms part of the posterior wall of the omental bursa and is a constituent of the stomach bed.
|
| |
|
|
| The left colic flexure |
|
- Lies on the lower part of the left kidney and the diaphragm, behind the stomach and below the lower pole of the spleen.
- It is slightly above the transpyloric plane.
- The phrenico- colic ligament is a horizontal fold of peritoneum attaching the flexure to the diaphragm opposite the 11 th rib in the midaxillary upper limit to the left paracolic gutter.
|
| |
|
|
| |
|

