The anal canal |
|
Position |
|
- Terminal part of the large intestines
- Extends from the anorectal angle
- Descends postero inferiorly between the anococcygeal ligament and the central perineal tendon
- Sorrounded the levator ani
|
|
Interior of the anal canal |
|
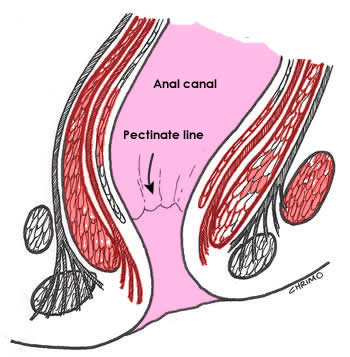 |
Anal colums:
- A series of longitudinal ridges / folds
- in the superior half of the mucous membrane of the anal canal.
- Contain terminal branches of superior rectal artery and vein
- The superior ends of the anal columns indicate the anorectal line where the anus joins the rectum
Anal pectinate line
- The inferior comb shaped limit of the anal valve.
- It indicates the site of junction of the superior part of the anal canal and inferior parts.
|
|
Sphincters |
|
|
The internal sphincter |
External sphincter |
- Involuntary
- Stimulated by parasympathetic nerves
- Sorrounds the superior 2/3rds of the anal canal
|
- Involuntary
- Supplied by S4 via the inferior rectal nerve
|
|
Anorectal ring |
|
Comprises of the following structures:
- Puborectalis muscle
- External anal sphincter
- A few involuntary fibres from the internal anal sphincter
It is responsible for maintaining anal continence
|
| |
| External anal sphincter |
|
 |
- Voluntary and surrounds the inferior end of the anal canal
- Lies in the perineum
- Has three parts
- Subcutaneous part (1)
(+) Consists of slender fibres
(+) Sorrounds the anus (crossing anterior and posterior to it)
(+) Has no bony attachments.
- Superficial part (2)
(+) Fibres extend anteriorly from:
the tip of the coccyx and the Anococcygeal ligament around the anus
to the central perineal tendon.
- Deep part (3)
(+) Arises from the central perineal tendon
(+) Fuses with the puborectalis part of the lavetor ani superiorly
(+) Blends with lavetor ani, and is not sharply distinguished from it.
- All the components are innervated by perineal branch of S4; and inferior rectal branch of the pudendal nerve.
|
|
Functions of the external anal sphincter; |
|
- Closes the anus
- Draws anal canal anteriorly, thereby increasing the anorectal angle.
- Deep fibres are assisted by puborectalis
|
| |
| |
|
Blood supply |
|
|
- Superior rectal – above pectinate line
- Inferior rectal – below pectinate line
- Middle rectal anastomoses the two
- The veins correspond
|
|
Lymphatics |
|
|
- Above the pectinate line – internal iliac- common iliac and aortic lymph nodes
- Below pectinate line – superficial inguinal – deep inguinal and then to iliac nodes
|
|
Innervation |
|
|
- The part above the pectinate receives autonomic innervation and is sensitive only to stretch
- The part below the pectinate line is innervated by inferior rectal branches of the pudendal nerve. This is somatic innervation and is sensitive to pain, touch and temperature
|
| |
| |
|

