| Blood supply to the abdomino-pelvic GIT | |
| |
|
| The coeliac trunk | |
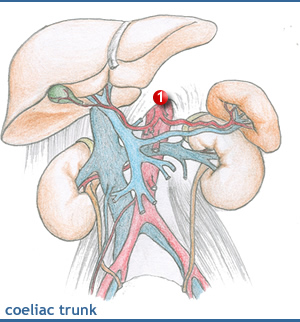 |
The coeliac trunk is the first and largest unpaired branch of the abdominal aorta. It arises opposite the body of L1, and just below the aorta hiatus. It is the artery of the foregut and supplies the alimentary canal from the lower third of the oesophagus to the middle of the descending part of the duodenum, as well as related gut derivatives (the liver, gall bladder and pancreas) and the spleen. |
| |
|
| Branches of the coeliac trunk | |
| Remember them from the 3 large organs they supply:- stomach, liver and spleen. 1) The left gastric artery gives off oesophageal branches, and then turns downwards to follow the lesser curvature where it forms an anastomosis with the right gastric artery. 2) The common hepatic artery passes below the omental foramen, giving off the right gastric and gastroduodenal arteries, and then ascends in the free edge of the lesser omentum, as the hepatic artery proper . The gastroduodenal artery gives rise to the superior pancreaticoduodenal, to supply the respective organs and the right gastroepiploic which runs on the greater curvature of the stomach, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery. 3) The splenic artery runs across the left suprarenal and left kidney and enters the splenorenal ligament and reaches the hilus of the spleen. It gives three main branches. |
|
| • Pancreatic branches supply
the pancreas. |
|
| |
|
| Superior mesenteric artery (SMA) | |
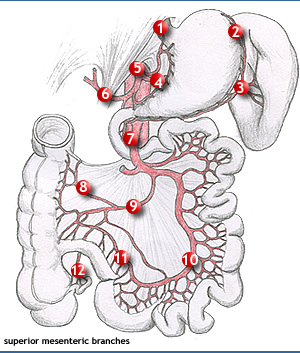 |
The superior mesenteric artery is found in the root of the mesentery at L2 near the midline, just below coeliac trunk. It is the artery of the midgut and supplies the GIT between greater duodenal papilla tto middle 1/3rd of transverse colon. Its branches include: a) Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery to supply the corresponding organs. b) Jejunal and ileal branches Anastomotic arcades between adjacent branches form secondary, tertiary and in the more distal parts even quaternary arcades. Vasa recta arise from the peripheral row of arcades. c) The ileocolic artery runs towards the ileocolic angle and divides into ascending and descending branches. It gives the appendidular artery, to the appendix. d) The right colic artery runs horizontally to the right and gives ascending and descending branches. e) The middle colic artery arises from the right side and descends in the mesocolon to upper border of the transverse colon, where it divides into right and left branches. |
| |
|
Home | Project Anatomy | Gross Anatomy | Topic Index | Chapter 33