| 25.1 Organisation of the pharynx |
| |
|
 |
Extents:
- 12 cm long
- from base of skull to body of C6
Relations:
- Anteriorly:
- Nasal cavity
- Nasal septum
- Oral cavity
- Larynx
- Posteriorly:
- Seperated from prevertebral fascia by retropharyngeal
space containing loose areolar tissue and pharyngeal venous plexus.
- Laterally:
- Neurovascular bundle of the neck and styloid
apparatus.
|
| |
|
| Pharyngeal
wall |
| Has 5 layers:
- Epithelium is pseudostratified columnar
ciliated epithelium in the nasal part, stratified squamous non keratinised
in the other parts,
- Subepithelial collections of lymphoid tissue.The large ones form tonsils.
- Lamina propria contains elastic tissue and mucous glands
- Submucosa:
Also contains elastic tissue, glands, blood vessels and nerves.
- Pharyngobasilar fascia:
Lines the internal surfaces of the pharyngeal muscles and attaches
the pharynx to the base of the skull, auditory tubes and to the lateral
margins of the posterior nasal apartures. Also fills the gap between
the skull and superior constrictor.
- Pharyngeal muscles:
Pharyngeal constrictors, circular (intrinsic) - and longitudinal (extrinsic).
What are the attachments?
- Bucopharyngeal fascia:
|
| |
|
| Divisions: |
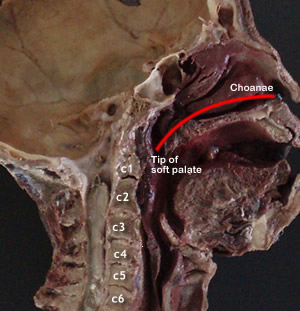
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
|
| |
|
| Nasopharynx (Postnasal
space) |
| |
Relations and Boundaries:
- Roof: Body
of sphenoid and basi-occiput
- Floor: Soft
palate
- Posterior:
Upper cervical vertebrae (C1, C2)
- Anterior:
Nasal cavity
- Laterally:
Eustachian tube, pharyngeal recess (fossa of Rosenmuller).
Note the tubal and pharyngeal tonsils.
Blood supply:
Pharyngeal branch of maxillary artery.
Innervation:
Pharyngeal branch of maxillary nerve
Clinical importance:
Common site of tumors (post nasal space of tumors). What are the
possible effects?
enlarged pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
What are the possible effects? |
| |
|
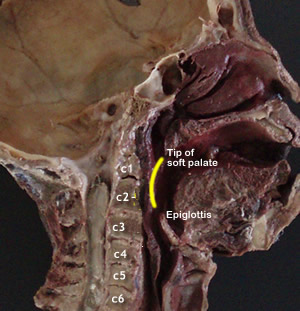
| Oropharynx (Pharynx
proper) |
| |
Relations and Boundaries:
- Anterior: Oral cavity
– palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches, palatine tonsils between
these.
- Superior: Soft palate.
- Inferior: Epiglottis.
- Posterior: C2, 3.
- Lateral: Neurovascular
bundle of neck.
Blood supply:
Pharyngeal branches of external carotid and maxillary lingual artery.
Innervation:
Glossopharyngeal.
Clinical importance:
Tonsillitis. |
| |
|
| Laryngopharynx |
|
|
Relations
and boundaries:
- Anterior: Larynx,
note piriform recess.
- Posterior:
c4,5,6
- Superior: Oropharynx
- Inferior: Esophagus
- Lateral: Neurovascular
structures of the neck
Blood supply:
Ascending pharyngeal, superior thyroid arteries
Innervation:
Vagus nerve
Clinical importance:
Foreign bodies in the piriform recess, pharyngeal diverticulae. |
| |
|