| The Midbrain | |
|
|
|
 |
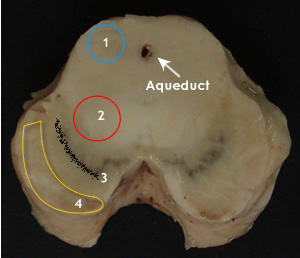
The central aqueduct is distinctive. Dorsal to this is the tectum with four colliculi.
Red nucleus is most distinctive in the midbrain tegmentum. It integrates information from cerebrum and cerebellum (involuntary motor control) Its fibers to the spinal cord (rubrospinal) transmit impulses that facilitate flexor muscle tone. Structures dorsal and lateral to the red nucleus form the midbrain reticular formation.
|
|
|
|
 |
The mibrain consists of four main parts:
Around the aqueduct is the periaqueductal gray. It contains nuclei of oculomotor and trochlear nerves. The most prominent structure in the tegmentum is the red nucleus but the tegmentum, also contains ascending tracts. The substantia nigra consits of melanin containing neurons tha regulate motor output of cerebral cortex Crus cerebri represents a bundle of projection fibers.
|
|
|
|
 |
The following structures can be identified In a cross section of the midbrain.
|
|
|
|
Blood supply to the midbrain
Vascular lesions of the midbrain include:
|
 Red area: shows area of vascular lesion involvement |
|
|