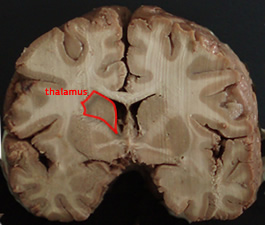
The Thalamus |
|
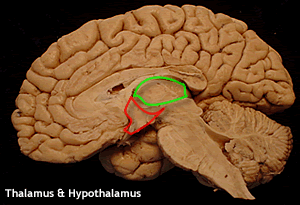 |
An egg shaped mass whose extent is:
The posterior enlarged part (pulvinar) overlies the midbrain. Structures related to its dorsal surface include:
It is joined with the opposite medially by interthalamic adhesion. The internal medullary lamina divides the thalamus into nuclear groups:
|
 |
|
| |
|
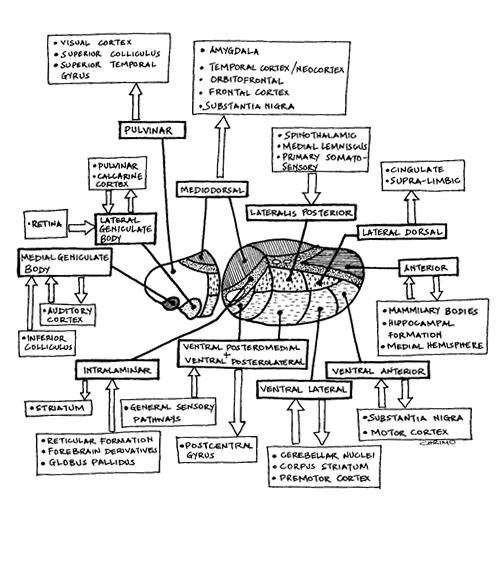
| Connections | |
 |
|
Functions:
|
|
| |
|
| Functions of specific nuclei: | |
|
 |