Damage to the pelvic diaphragm
 May be caused by May be caused by
- Damage during un assisted delivery
- Episiotomy
- Nerve damage/ nerve injury
 Weakens support for pelvic viscera.These viscera may herniate out e.g. Weakens support for pelvic viscera.These viscera may herniate out e.g.
- Cystocele; herniation of the urinary bladder
- Cystourethrocele; herniation of the urinary bladder and urethra
- Rectocele; herniation of the rectum
- Uterine prolapse; herniation of the uterus
 When mild: the support of the urethra and ano-rectum is impaired even though the organs may not herniated. When mild: the support of the urethra and ano-rectum is impaired even though the organs may not herniated.
This results in stress incontinence of both urine and stool, more for the urine, whenever the intra abdominal
pressure is raised .e.g. during coughing or sneezing.
Ischio anal abscess
 A collection of pus in the fossa due to infection A collection of pus in the fossa due to infection
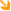 Infection may reach this fossa Infection may reach this fossa
- Following infection in the anus
- From extension of a pelvi-rectal abscess
- Following a tear in the anal mucosal membrane
- From a penetrating wound in the anal region.
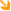 Are best managed by surgical incision and drainage. If this is not done, the abscess may spontaneously open into; Are best managed by surgical incision and drainage. If this is not done, the abscess may spontaneously open into;
- Anal canal
- Rectum
- Skin in the perineum
- Spread to opposite side
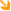 Pundendal block anaesthesia. Pundendal block anaesthesia.
- Pundendal blocks are done to relieve pain in the perineum, e.g. during labor and especially when an episiotomy is required.
- A local anaesthetic agent is injected into the tissues surrounding the pundendal nerve in the pundendal canal.
- The injection is usually made where the nerve crosses the lateral aspect of the sacrospinous ligament near its attachment to the ischial spine, which is good landmark.
|