Parotid region |
Introduction |
Part of the face infront of the ear and below the zygomatic arch . Principal structures in this area are:
|
|
Masseter Muscle |
 |
A muscle of mastication.
Origin: Lower margin of the zygomatic arch
Insertion: Lateral surface of the mandibular ramus.
Blood supply: Branches of facial , maxillary and superficial temporal arteries
Innervation: Masseteric branch of mandibular nerve
Action: Elevates and draws forwards the angle of the mandible when the jaws are approximated. |
|
|
 |
 Position: Position:
- Side of the face
- Anterior to the ear
- Extents from the zygomatic arch to the upper part of the neck
- Below the external auditory meatus on to the mastoid process
- Overlies masseter muscle
|
|
 Surfaces & Relations Surfaces & Relations |
|
Lateral (superficial) surface: |
Postero superior |
Medial: |
Posteromedial surface: |
Anteromedial surface: |
| |
| covered by skin and superficial fascia. |
|
- Styloid apparatus
- Carotid sheath and it contents
- Facial nerve trunk
|
- Mastoid process,
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle.
|
- Posterior border of mandibular ramus
- Masseter muscle
- Medial pterygoid muscle
|
| |
|
|
| Parotid bed |
|
The deep lamina of the gland lies on it.
It comprises of:
- mastoid process and the sternocleidomastoid muscle
- the ramus of the mandible and the masseter muscle
- the styloid apparatus
- the EAM grooves the upper border
|
|
| Structures traversing the gland |
|
 |
- external carotid artery
- facial nerve
- retromandibular vein
- parotid (pre ocular) lymph nodes
|
|
| The Parotid Duct (of stensen) |
|
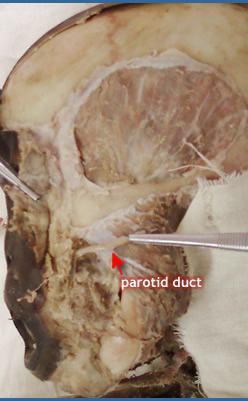 |
Course
- Across masseter
- Pierces buccinator
- Lies on the middle third of a line between the intertragic notch of the auricle and the midpoint of the philtrum
Termination
- Mucous membrane opposite the second upper molar tooth.
|
|
| Blood supply |
|
- Branches of superficial temporal artery
- Some twigs from maxillary
- Veins drain to the retromandibular vein
|
|
| Lymphatic drainage : nodes |
- Pre auricular
- Post auricular
- Sub mandibular
- Upper deep cervical
|
|
| Nerve supply |
|
Parasympathetic
- Preganglionic fibres arise from cell bodies in the inferior salivary nucleus in the medulla,
- Fibres travel by way of the glossopharyngeal nerve, its tympanic branch, the tymphanic plexus and the lesser petrosal nerve
- Synapse in otic ganglion.
- Post ganglionic fibres travel through auriculo temporal nerve
General sensory
- Auriculo-temporal nerve
- Greater Auricular nerve
Symphathetic
- Superior cervical ganglion by way of the plexus on the external carotid and middle meningeal arteries.
|
|
|



