Hand Joints |
|
Wrist joint (radiocarpal articulation) |
|
| Classification: |
|
|

|
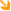 Synovial ellipsoid joint Synovial ellipsoid joint |
 |
|
|
Articular surfaces: |
|
|

|
Concave ellipsoid distal surface of radius and articular disc
Convex proximal surfaces of :
- Triquetral(1)
- Lunate(2)
- Scaphoid(3) bones
|
 |
| |
|
Capsule: |
|
|
 |
Surrounds the joint and is thickened to form palmar, dorsal and collateralligaments |
| |
|
Innervation: |
|
|
Posterior and anterior interosseous nerves |
|
| Blood Supply |
|
| Carpal rete: Ventral and dorsal network |
|
|
Movements: |
|
|
 |
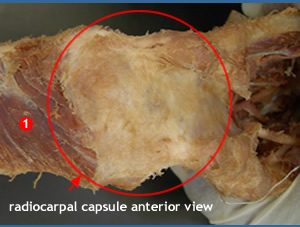
Flexion |
 |
Extension |
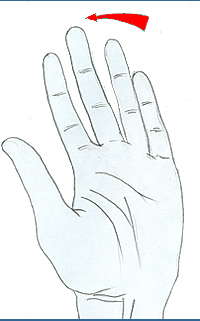 |
radial abduction |
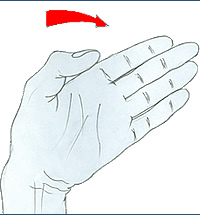 |
ulnar adduction |
Movements accompanied by those at midcarpal joint
Total range of flexion 80° , of extension 60°
More flexion at midcarpal joint while more extension at wrist joint
Range of abduction 15° , range of adduction 45° . Why the difference? |
| |
Movements produced by: |
Movement |
Muscle |
Flexion |
flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris, flexors of Fingers and thumb |
Extension |
Radial extensors, ulnar extensor, extensors of fingers and thumb |
Abduction |
Flexor carpi radialis, two radial extensors, abductor pollicis longus |
Adduction |
flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
Intercarpal joints |
|
|
- Synovial
- Intercarpal ligaments connect the bones. Flexor retinaculum is an accessory intercarpal ligament
- Thin capsule
- Synovial cavity may communicate with radiocarpal joint
- Midcarpal joint is a compound sellar joint between the proximal and distal row of carpal bones
- Carpometacarpal joints often communicate with intercarpal joints
|
 |
|
|
|
- The 1 st carpometacarpal joint of the thumb is a saddle joint between trapezium and 1 st metacarpal. Opposition occurs here. It has a loose and lax capsule allowing ranges of movement
|
|
Metacarpophalangeal joints |
|
|
- Synovial joints allowing flexion, extension, abduction and adduction
- Palmar ligaments limit extension
- Transverse metacarpal ligaments are additional stability
- Collateral ligaments flank the joints
|
|
Interphalangeal joints |
|
| |
- Uniaxial
- Capsule
- Extension is limited by palmar and collateral ligaments
|
|
1st Carpometacarpophalangeal Joint |
|
|
Classification
- Synovial joint of sellar variety
Articular surfaces
- 1st metacarpal base and trapezium
Reasons for increased mobility
- Extensive articular surfaces and their shape
- Laxity of the capsule
- Obliquity of ligaments
Capsular attachments
From: Circumference of metacarpal base
To: Rim of distal trapezial articular facet
Capsule is thickest laterally and dorsally
Ligaments
Lateral ligament: From lateral surface of trapezium to radial side of metacarpal base
Palmar and dorsal ligaments: From palmar and dorsal surfaces of trapezium to ulnar side of metacarpal base
Relations
Palmar surface:
Thenar muscles
Dorsal surface:
Long and short extensors
Medial:
1st dorsal interosseous
Tendon of flexor pollicis longus
Lateral
- Tendons of abductor pollicis longus
- Extensor pollicis brevis
Movements
Movement |
Muscles |
Innervation |
Flexion |
Flexor pollicis brevis
Opponens brevis
Flexor pollicis longus |
Median nerve |
Extension |
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis brevis and longus |
Radial N. |
Abduction |
Abductor pollicis longus and brevis |
Radial N. |
Adduction |
Adductor pollicis |
Radial N. |
Opposition |
Opponens pollicis |
Ulnar N. |
Circumduction |
All above muscles |
All nerves |
|
|
|
Innervation
- Radial n.
- Median n.
- Ulna n.
Blood supply
- Branches of radial artery
|
|








