Dorsum of Foot |
|||||||
| Cutaneuos nerves | |||||||
Medial margin : Saphenous nerve |
|||||||
Dorsalis Pedis artery |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Dorsal venous arch | |||||||
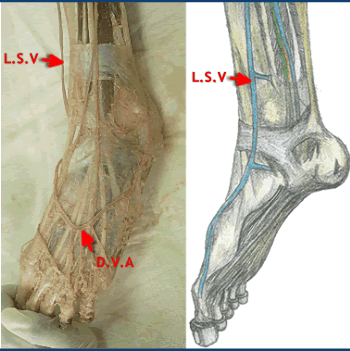 |
Lies over the heads of metatarsals
Joins medial dorsal digital vein medially to form great saphenous vein (Dorsal Venous arc [D.V.A] forming the long saphenous vein [L.S.V] on the medial side of the foot ) |
||||||
| Inferior extensor retinaculum | |||||||
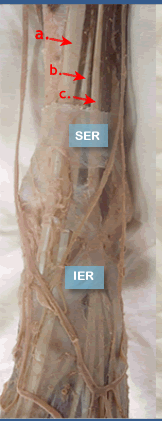 |
Inferior Extensor Retinaculum (IER) Superior Extensor Retinaculum (SER)
|
||||||